Rsau/enable: Set to 1 to activates audit logging rsau/local/file: Name and location of the audit log file rsau/maxdiskspace/local: Max. Space of the audit file. If maximum size is reached auditing stops. Rsau/selectionslots: Max. Number of filters. The settings are activated after the instance has been restarted. Defining Filters. D) rsau/local/file 10. Which profile parameter should be adjusted to prevent users from losing their authorizations during profile generation and when importing profiles and/or roles?
To the DEFAULT.PFL file in the location sysprofile, add. Rsau/enable = 1; rsau/local/file = /audit00; Note: The user should have permission to read this audit file while importing. Db2 database systems allow auditing at. Rsau/local/file path to audit log file. Rsau/maxdiskspace/local maximum space to allocate for the audit files. Rsau/selectionslots 3.
Rsau/local/file
Transaction ST22 -view ABAP-system dumps. You can via the menu
You can enable Security Audit Log system. From this you can see log successful
There is also an option to activate auditing changes in tables. Write the profile parameter rec/client = XXX (client number).You can specify multiple
Rsau Local File Online
Rsau Local File Bankruptcy
Resolution:
Turn on Security Audit Logging using SM19,and review the audit logs using SM20.Use a filter to log everything available for a particular user id. Analyzethe logs in SM20 for that user ID.
Pay attention to the terminal being used. If you see more than oneterminal, it could be someone else trying to use the id. Also dependingon what the application is for, it might be necessary to change the userID to type System to resolve locks or expired passwords for a non-dialoguser in some cases.
Specifically when a non SAP application is able to change the pw ofa non dialog id. There is documentation on setting up SAP Security auditlogs. It is not difficult. You can even have a CCMS log agent email youin real time if log entries are showing up in the audit logs for that IDand catch the person in the act or identify the underlying cause.
You should also consider reviewing RFC logs. Turn up the verbosityof the trace and you can see alot of details when the id is being usedin RFC scenarios.
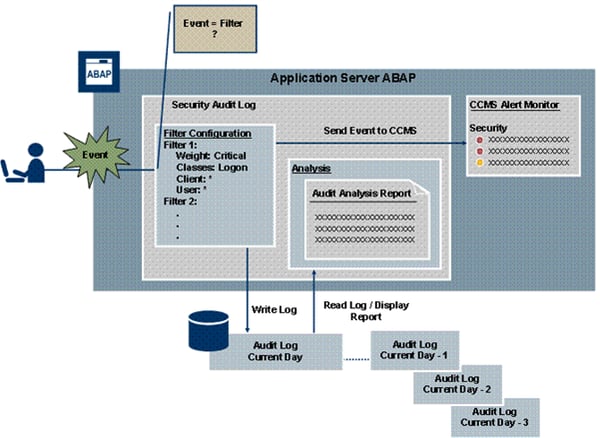
SAP Security Audit Logs
SAP R/3 supports an internal auditing system, called the Security AuditLog. Each SAP application server maintains a daily audit file. You canspecify the name and location of the Security Audit Log using the rsau/local/fileprofile parameter.
To activate the internal audit system, set the audit log parametersas described in the following table :
Audit Log parameter settings Audit Log Parameter Set value to...
rsau/enable 1
rsau/local/file path to audit log file
rsau/max_diskspace/local maximum space to allocate for the audit files
rsau/selection_slots 3
rec/client ALL
Note:
The rsau/local/file parameter contains the entire path name to theaudit logs, as well as the file name. The file name must include + symbolsto contain a variable datepart. Do not include a file extension in thefile name. See the following examples for clarification.
This example shows a valid path and filename:
/usr/sap/machine1/log/audit_++++++++
This example shows an invalid path and filename; the filename doesnot include a datepart:
/usr/sap/machine1/log/audit
This example shows an invalid path and filename; the filename includesa file extension:
/usr/sap/machine1/log/audit_++++++++.aud
After you set the audit log profile parameters, start transaction SM19to specify which events to log in the Audit Security Log.
